www.michael-buhlmann.de
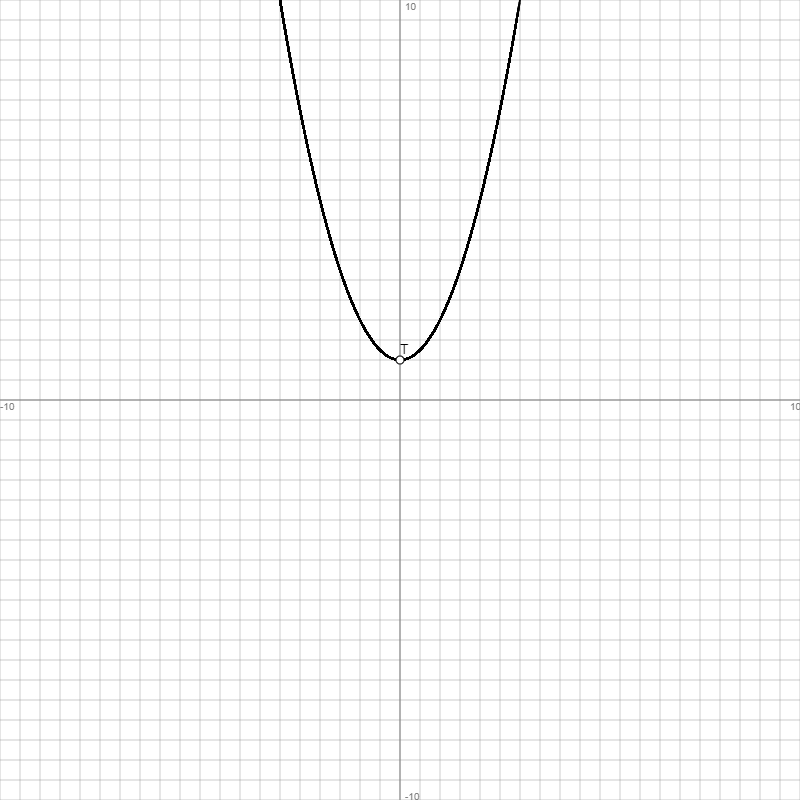
Funktion: f(x) = x2 + 1, Df = R, Wf = [1; +∞), entlang der y-Achse nach oben verschobene Normalparabel, Funktion achsensymmetrisch zur Senkrechten x = 0, x -> -∞: f(x) -> +∞, x -> +∞: f(x) -> +∞ ->
| Wertetabelle: | |||||
| x | f(x) | f'(x) | f''(x) | f'''(x) | Besondere Kurvenpunkte |
| -10 | 101 | -20 | 2 | 0 | |
| -9.5 | 91.25 | -19 | 2 | 0 | |
| -9 | 82 | -18 | 2 | 0 | |
| -8.5 | 73.25 | -17 | 2 | 0 | |
| -8 | 65 | -16 | 2 | 0 | |
| -7.5 | 57.25 | -15 | 2 | 0 | |
| -7 | 50 | -14 | 2 | 0 | |
| -6.5 | 43.25 | -13 | 2 | 0 | |
| -6 | 37 | -12 | 2 | 0 | |
| -5.5 | 31.25 | -11 | 2 | 0 | |
| -5 | 26 | -10 | 2 | 0 | |
| -4.5 | 21.25 | -9 | 2 | 0 | |
| -4 | 17 | -8 | 2 | 0 | |
| -3.5 | 13.25 | -7 | 2 | 0 | |
| -3 | 10 | -6 | 2 | 0 | |
| -2.5 | 7.25 | -5 | 2 | 0 | |
| -2 | 5 | -4 | 2 | 0 | |
| -1.5 | 3.25 | -3 | 2 | 0 | |
| -1 | 2 | -2 | 2 | 0 | |
| -0.5 | 1.25 | -1 | 2 | 0 | |
| 0 | 1 | 0 | 2 | 0 | Schnittpunkt Sy(0|1) = Tiefpunkt T(0|1) |
| 0.5 | 1.25 | 1 | 2 | 0 | |
| 1 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 0 | |
| 1.5 | 3.25 | 3 | 2 | 0 | |
| 2 | 5 | 4 | 2 | 0 | |
| 2.5 | 7.25 | 5 | 2 | 0 | |
| 3 | 10 | 6 | 2 | 0 | |
| 3.5 | 13.25 | 7 | 2 | 0 | |
| 4 | 17 | 8 | 2 | 0 | |
| 4.5 | 21.25 | 9 | 2 | 0 | |
| 5 | 26 | 10 | 2 | 0 | |
| 5.5 | 31.25 | 11 | 2 | 0 | |
| 6 | 37 | 12 | 2 | 0 | |
| 6.5 | 43.25 | 13 | 2 | 0 | |
| 7 | 50 | 14 | 2 | 0 | |
| 7.5 | 57.25 | 15 | 2 | 0 | |
| 8 | 65 | 16 | 2 | 0 | |
| 8.5 | 73.25 | 17 | 2 | 0 | |
| 9 | 82 | 18 | 2 | 0 | |
| 9.5 | 91.25 | 19 | 2 | 0 | |
| 10 | 101 | 20 | 2 | 0 | |
| Graph: | |||||
 | |||||
Abkürzungen: Df = (maximaler) Definitionsbereich, f(x) = Funktion, f'(x) = 1. Ableitung, f''(x) = 2. Ableitung, f'''(x) = 3. Ableitung, H = Hochpunkt, N = Nullstelle, P = Polstelle, R = reelle Zahlen, T = Tiefpunkt, W = Wendepunkt, WS = Sattelpunkt, Wf = Wertebereich, {.} = ein-/mehrelementige Menge, [.; .] = abgeschlossenes Intervall, (.; .) = offenes Intervall, [.; .), (.; .] = halboffenes Intervall, ∞ = unendlich.
Bearbeiter: Michael Buhlmann