www.michael-
buhlmann.de
Mathematik
> Integralgleichung
Integralgleichung I (Bestimmung der oberen Grenze)
|
Bestimmtes Integral einer integrierbaren Funktion f(x) auf einem Intervall [a; ξ], Integralwert A -> Integralgleichung Funktionseingabe (gemäß JavaScript): Variable x, Klammern (), Addition +, Subtraktion -, Multiplikation *, Division /,
Betrag |x| = |
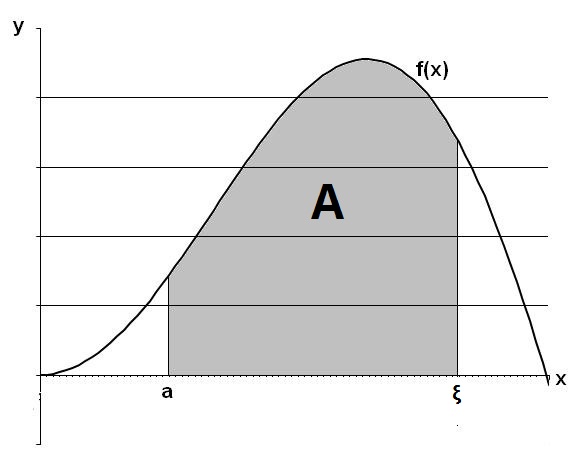 |
Eingabe von Funktion, unterer Grenze, Integralwert (Dezimalzahlen mit Punkt statt Komma):