www.michael-br />buhlmann.dee
Mathematik
> Tangenten und Normalen
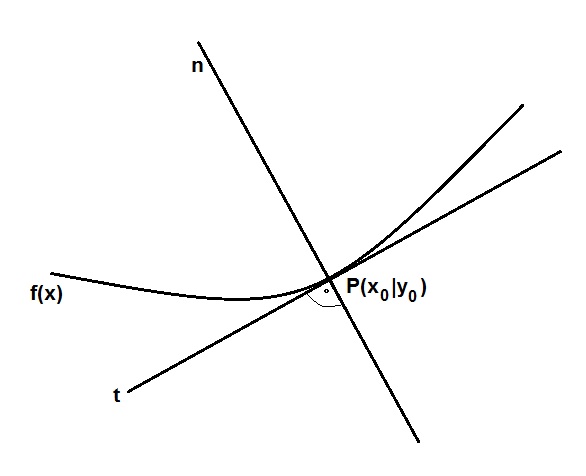
Funktionen-Normalenplotter II
|
Abbildung:
Funktionseingabe (gemäß JavaScript): Variable x, Klammern (), Addition +, Subtraktion -, Multiplikation *, Division /,
Betrag |x| = |
 |
Eingabe von Funktion, x-Wert (Dezimalzahlen mit Punkt statt Komma, Bruch in der Form Zähler/Nenner):